A root canal is a treatment used to repair and save a tooth that is badly decayed or infected. A tooth’s nerve and pulp can become irritated, inflamed, and infected due to deep decay; repeated dental procedures on a tooth; or large fillings, a crack, or chip in the tooth. It also can happen because of trauma to the face.
Root canal procedures have the reputation of being painful. But the procedure itself is no more painful than having a filling placed.
Pediatric dentists work hard to keep the smiles of kids bright and healthy. When a dental visit is a positive experience. children may be happy to return every six months for their checkup. And for that, parents will be grateful.
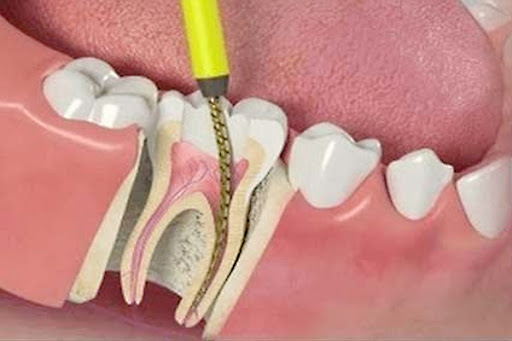
During a root canal procedure, the nerve and pulp of the tooth are removed and the inside is cleaned and sealed. Without treatment, the tissue surrounding the tooth will become infected and an abscess may form.
A tooth’s nerve is not vitally important to a tooth’s health and function after the tooth has come through the gums. Its only function is sensory – to give the sensation of hot or cold. The absence of a nerve won’t affect how your tooth works.
Root canal procedures have the reputation of being painful. But the procedure itself is no more painful than having a filling placed.
Then a tooth’s nerve tissue or pulp is damaged, it breaks down and bacteria begin to multiply within the pulp chamber. The bacteria and other decayed debris can cause an infection or abscessed tooth. An abscess is a pus-filled pocket that forms at the end of the roots of the tooth. An abscess happens when the infection spreads all the way past the ends of the roots of the tooth. An infection in the root canal of a tooth can also cause:
Swelling that may spread to other areas of the face, neck, or head
1. Bone loss around the tip of the root.
2. Drainage problems extending outward from the root. A hole can occur through the side of the tooth with drainage into the gums or through the cheek with drainage into the skin.
If you need a root canal, you may notice these signs:
1. Tooth sensitivity that lingers, especially to heat or cold.
2. Sharp pain when chewing or biting.
3. Pimples on your gums.
4. Chipped or cracked teeth.
5. Swollen or painful gums.
6. Deep decay or darkened gums.
1. Infant oral health exams.
2. Distribution of relaxation medications.
3. Special counseling on nutrition.
4. Emergency dental care.
5. Space management after the premature loss of a primary tooth.
6. Discouragement of thumb and finger sucking through appliances and methods.